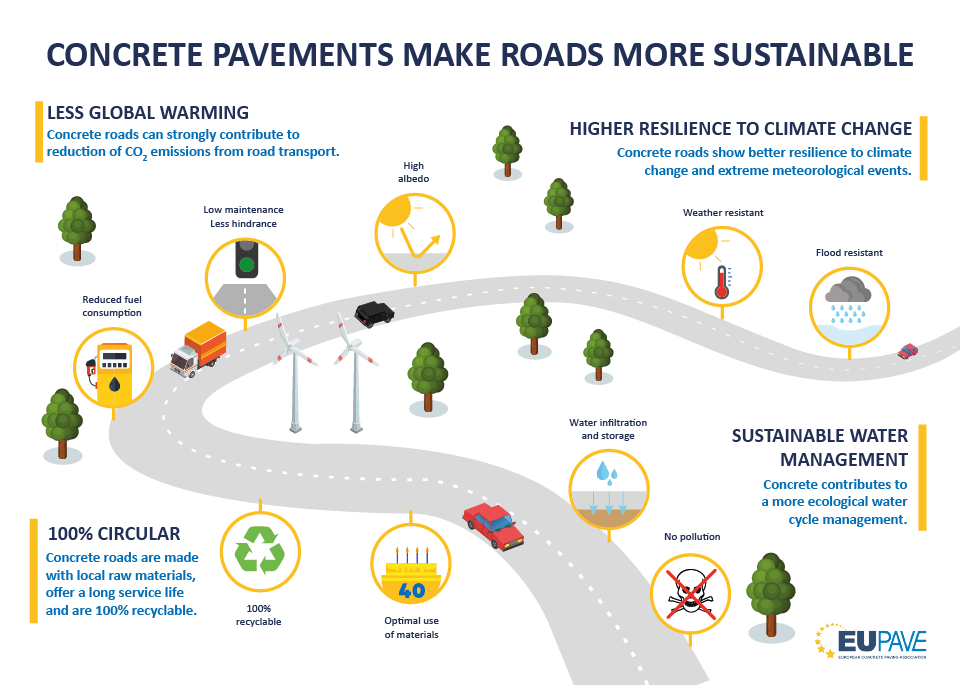
Concrete roads require minimum maintenance work, thereby causing less traffic jams.
Vehicles consume up to 6% less fuel when riding upon smooth and non-deformable road surfaces.
Light coloured concrete surfaces have a high light reflection, which counteracts global warming.
Changing from asphalt to concrete equals a reduction of 25 to 38 kg CO2/m2
 Find more information on the albedo impact in our publication "Concrete roads: a smart and sustainable choice"
Find more information on the albedo impact in our publication "Concrete roads: a smart and sustainable choice"







